
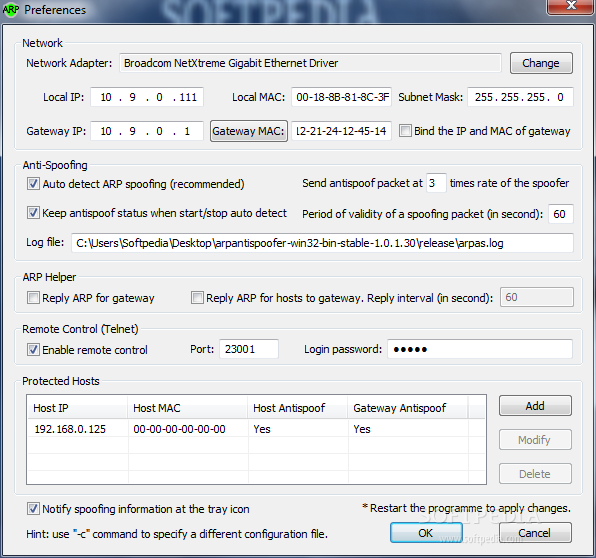
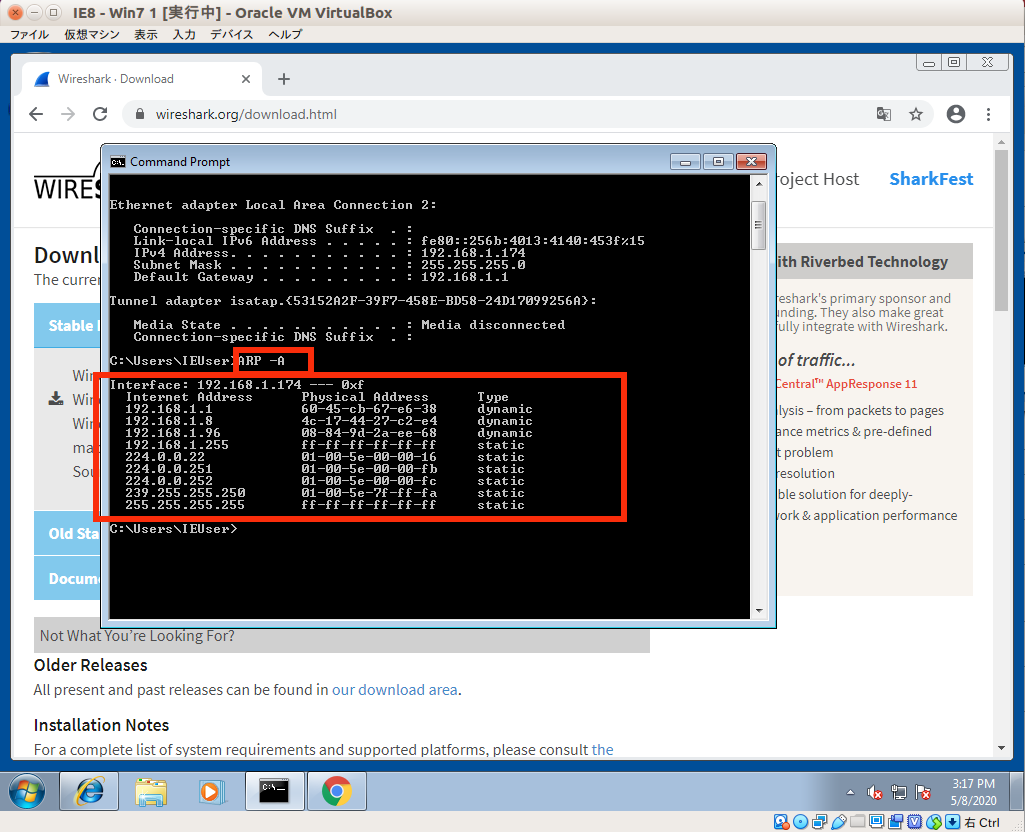
In this experiment, Alice and Bob are connected to a WiFi hotspot, and wish to communicate with one another. The attack we're going to try involves a different approach, using a technique known as ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning. Other clients on the same access point can capture the traffic, but can't necessarily decrypt it - to decrypt the traffic, a malicious attacker would have had to either capture the initial handshake between client and AP (when the keys were set up), or force the client to disconnect and reconnect, and capture the new handshake between client and AP.

When data is sent over a WiFi network using WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK security, it is encrypted at Layer 2 with per-client, per-session keys, and may be decrypted only by its destination. This experiment shows how a malicious attacker can act as a "man in the middle" to capture traffic on a WiFi hotspot, including potentially sensitive material such as login credentials and private web browsing.Ī man in the middle (MITM) attack is one where the attacker (in our example, Mallory) secretly captures and relays communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other (in our example, Alice and Bob.) (Alternatively, you can use "sb4" testbed at ORBIT, with some modifications to the instructions.) Finally, you must have reserved time on either the outdoor testbed at ORBIT or the WITest testbed, and you must run this experiment during your reserved time. The project lead of the project you belong to must have enabled wireless for the project. You should have already uploaded your SSH keys to the portal. To reproduce this experiment on GENI, you will need an account on the GENI Portal, and you will need to have joined a project. This experiment uses wireless resources (specifically, the "outdoor" testbed on ORBIT, or the WITest testbed), and you can only use wireless resources on GENI during a reservation. It should take about 60-120 minutes to run this experiment, but you will need to have reserved that time in advance. This experiment shows how an attacker can use a simple man-in-the-middle attack to capture and view traffic that is transmitted through a WiFi hotspot. Menu Run a Man-in-the-Middle attack on a WiFi hotspot Fraida FundĠ6 March 2016 on education, security, wireless, 802.11


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
